The Allure of the Orb: Crafting Circles and Why We're Obsessed
From the humble pizza to the grand celestial bodies, circles are everywhere. But have you ever stopped to consider the act of *creating* a circle? It's more profound than you might think. This isn't a geometry lesson; it's an exploration of the inherent human fascination with roundness, a journey into the very essence of cyclical perfection.
We're talking about crafting circles, not just identifying them. How do you conjure this perfect shape? The question itself sparks a quiet thrill, a sense of playful challenge. Think about it – the gentle sweep of a compass, the steady rotation of a potter’s wheel, even the careful swirl of a barista creating latte art. These are all acts of circle-making, moments of deliberate artistry that often go unnoticed.
The history of circle making is as old as humanity itself. Early humans observed the moon, the sun, and the cyclical nature of life, associating the circle with wholeness and continuity. From cave paintings depicting circular forms to the invention of the wheel, our ancestors recognized the power and utility of this fundamental shape. Constructing circles became essential for everything from building shelters to creating tools and understanding the movement of the stars.
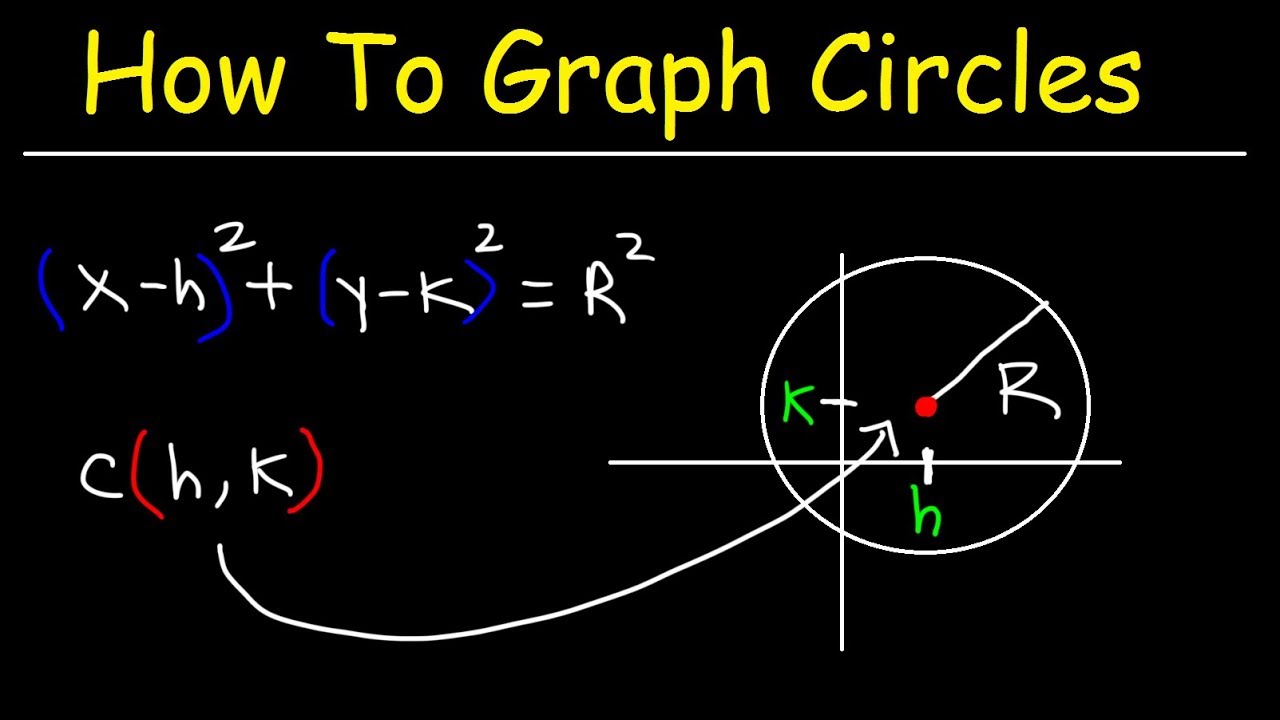
One of the key issues in circle creation is achieving true precision. While drawing a roughly circular shape is easy enough, creating a perfectly symmetrical circle requires specific tools and techniques. The challenge lies in maintaining a constant radius and ensuring a smooth, unbroken line. This quest for perfect roundness has fueled innovation throughout history, leading to the development of tools like the compass and sophisticated mathematical formulas.
But why are we so drawn to circles? Beyond their practical applications, circles hold symbolic significance across cultures. They represent unity, infinity, and the cyclical nature of time. Think of wedding rings, mandalas, and the circular patterns found in nature. These associations imbue the circle with a powerful emotional resonance, making the act of creating one even more compelling.
Creating a circle can be accomplished in several ways. Using a compass is the most common method for drawing precise circles. Alternatively, one can use stencils or trace around circular objects. In digital environments, software programs offer tools for creating perfect circles with ease. Even freehand drawing, while less precise, can be a satisfying way to explore the form.
Three key benefits of understanding circle creation are enhanced spatial reasoning, improved artistic skills, and a deeper appreciation for geometry and mathematics. For example, understanding how a compass works strengthens spatial reasoning, while practicing circle drawing improves fine motor skills and artistic expression. Furthermore, exploring the mathematical properties of circles lays a foundation for more advanced concepts in geometry and trigonometry.
To create a perfect circle with a compass, place the sharp point firmly on your paper. Adjust the compass to your desired radius. Holding the compass steady at the top, rotate the pencil end around the point, applying gentle pressure. Maintain a consistent speed and pressure to ensure a smooth, unbroken line.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Different Circle Making Methods
| Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Compass | Precision, control over radius | Requires specific tool, can be difficult on uneven surfaces |
| Stencil | Easy to use, quick | Limited to available stencil sizes |
| Freehand | Accessible, requires no tools | Lack of precision |
Five best practices for using a compass: 1. Ensure the compass point is sharp. 2. Use a stable surface. 3. Hold the compass at the top, not the arms. 4. Apply consistent pressure. 5. Rotate the compass in a smooth, continuous motion.
Five real-world examples of circles: wheels, clocks, coins, plates, and the iris of the eye.
Five common challenges and solutions in circle creation: inconsistent pressure (solution: practice and steady hand), difficulty maintaining a constant radius (solution: high-quality compass), compass slipping on the paper (solution: use a textured paper or a compass with a non-slip base), uneven circle (solution: check compass point and pressure), and difficulty drawing large circles (solution: beam compass).
FAQ: 1. What is a circle? 2. How do I use a compass? 3. What are some real-world examples of circles? 4. How do I draw a circle freehand? 5. What is the radius of a circle? 6. What is the diameter of a circle? 7. How do I calculate the circumference of a circle? 8. How do I calculate the area of a circle?
Tips for circle mastery: Practice makes perfect! Experiment with different tools and techniques. Don't be afraid to embrace imperfections, even in the pursuit of perfect roundness.
The seemingly simple act of creating a circle is a journey through history, mathematics, and artistic expression. From its ancient origins to modern applications, the circle continues to fascinate and inspire. Whether you're using a compass, a stencil, or simply your hand, the act of crafting a circle connects you to a long lineage of human ingenuity and creativity. By understanding the methods, appreciating the symbolism, and practicing the techniques, you unlock not only the ability to create a perfect circle but also a deeper appreciation for the world around us. So, grab a pencil, a compass, or even a cup of coffee, and explore the magic of the circle. You might be surprised at what you discover.
Conquer your monday blues the power of motivational memes
What that lump on your dogs bottom could mean
The intriguing symbolism of hand clock tattoos a journey through time