Unveiling the Power of Grade 8 Fine Thread Bolt Torque Specifications
In the intricate dance of engineering and construction, where forces meet and materials strain, the humble bolt plays a pivotal role. But not all bolts are created equal. Among them, the grade 8 fine thread bolt stands out, a testament to precision and strength. Understanding its torque specifications is not merely a technical detail; it's the key to unlocking its full potential, ensuring structural integrity, and preventing catastrophic failures. This exploration delves into the world of grade 8 fine thread bolt torque, unraveling its significance and offering practical guidance for its proper application.
Imagine a world without standardized fasteners. A world where every bolt is a unique snowflake, its strength and tightening requirements a mystery. Chaos would reign in construction, manufacturing, and countless other industries. The grade 8 fine thread bolt, with its well-defined torque specifications, offers a beacon of order in this potential chaos. It represents a promise of reliability, a guarantee of predictable performance under stress.
The history of standardized bolt torque specifications is intertwined with the rise of industrialization. As machines became more complex and structures more ambitious, the need for reliable fasteners became paramount. The development of standardized grades, including grade 8, marked a significant step forward, allowing engineers to specify fasteners with confidence, knowing their mechanical properties and performance characteristics. Fine threads, offering increased tensile strength and resistance to loosening, further refined this system, providing a solution for applications demanding high performance.
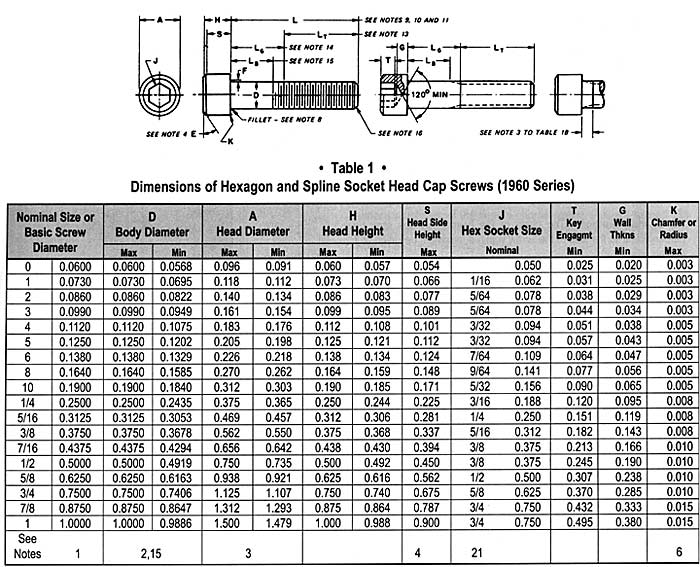
The significance of a grade 8 fine thread bolt torque chart cannot be overstated. It's the Rosetta Stone for understanding how much rotational force is needed to achieve the optimal clamping force for a given bolt size and material. Under-torquing can lead to joint separation and failure, while over-torquing can strip threads or even fracture the bolt, compromising the integrity of the entire assembly. The torque chart serves as a crucial guide, navigating the delicate balance between too loose and too tight.
Accessing and interpreting a grade 8 fine thread bolt torque chart is essential for anyone working with these fasteners. These charts, readily available online and in engineering handbooks, typically list bolt diameter, thread pitch, and recommended torque values for both lubricated and dry conditions. Understanding these variables and selecting the appropriate values is crucial for achieving the desired clamping force and ensuring the long-term reliability of the bolted joint.
One of the primary benefits of using a grade 8 fine thread bolt torque chart is the prevention of fastener failure. By adhering to the recommended torque values, you minimize the risk of stripped threads, broken bolts, and joint separation, ensuring the structural integrity of the assembly.
Another advantage is improved joint performance. Proper torquing maximizes the clamping force, distributing the load evenly across the joint and preventing loosening under vibration or dynamic loads. This enhanced performance is crucial in critical applications where joint failure can have serious consequences.
Furthermore, utilizing a torque chart contributes to increased efficiency and reduced costs. By preventing fastener failures and rework, you save time and resources, streamlining the assembly process and minimizing downtime.
Best Practices for Using Grade 8 Fine Thread Bolt Torque Specifications:
1. Always consult the appropriate torque chart for the specific bolt size, thread pitch, and lubrication condition.
2. Use a calibrated torque wrench to ensure accurate application of torque.
3. Clean and lubricate the threads before tightening the bolt.
4. Tighten the bolts in a sequence recommended by the manufacturer or engineering standards.
5. Regularly inspect bolted joints for signs of loosening or damage.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Fine Thread Bolts
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Higher tensile strength | More prone to stripping if over-torqued |
| Better resistance to loosening | Require more precise torque control |
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What is the difference between grade 5 and grade 8 bolts? Grade 8 bolts are stronger.
2. What is the purpose of a torque chart? To provide proper torque specifications.
3. How do I choose the right torque value? Based on bolt size and thread pitch.
4. What is the importance of lubrication? It reduces friction and allows for accurate torque.
5. How can I prevent over-torquing? Use a calibrated torque wrench.
6. What are the consequences of under-torquing? Joint separation and failure.
7. How often should I inspect bolted joints? Regularly, based on the application.
8. Where can I find a grade 8 fine thread bolt torque chart? Online and in engineering handbooks.
In conclusion, understanding and applying the correct torque specifications for grade 8 fine thread bolts is fundamental to ensuring the safety, reliability, and longevity of any assembly. By consulting the appropriate torque charts, using calibrated tools, and following best practices, you can harness the full potential of these high-strength fasteners and avoid the pitfalls of improper torquing. This knowledge empowers you to build with confidence, knowing that your structures are secure and your machines will perform as intended. The proper use of a grade 8 fine thread bolt torque chart transforms a seemingly mundane task into an act of precision engineering, contributing to a world where structures stand strong and machines hum with efficiency.
The power of unity exploring filipino poems on togetherness
Elevating traditions cartoon duit raya packet templates
Maximizing space clever small bathroom layout ideas for 5 x 7 rooms