Unlocking the Secrets of the Evaporator: How It Works and Why It Matters
Ever wonder how that frosty magic happens inside your fridge, or how that swamp cooler keeps you comfortable on a scorching day? The secret lies in a humble yet powerful component: the evaporator. Understanding the evaporator's purpose is like unlocking a key to a world of efficient cooling and industrial processes.
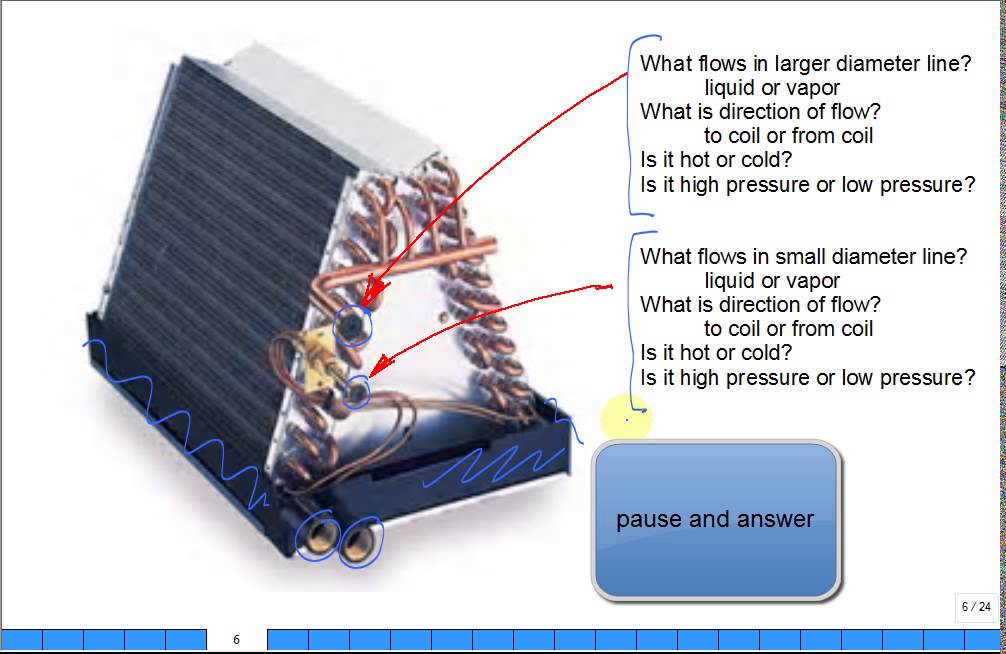
An evaporator's primary function is to absorb heat from its surroundings. It does this by utilizing a refrigerant, a special fluid that readily changes between liquid and gaseous states. As the liquid refrigerant flows into the evaporator, it absorbs heat and vaporizes, effectively cooling the surrounding area. This chilled air or liquid is then circulated, providing the desired cooling effect.
The principle behind evaporation has been around for centuries, with early forms used for cooling and concentrating liquids. From simple earthenware pots used for water cooling to sophisticated industrial systems, the core principle remains the same: exploiting the heat-absorbing properties of a liquid changing to a gas. Modern evaporators are essential in diverse applications, from refrigeration and air conditioning to industrial processes like chemical concentration and water purification.
The importance of the evaporator's function cannot be overstated. It plays a critical role in preserving food, maintaining comfortable living and working spaces, and enabling numerous industrial processes. However, issues such as refrigerant leaks, coil fouling, and inefficient operation can hamper evaporator performance, highlighting the importance of proper maintenance and understanding of its operation.
For example, in a refrigerator, the evaporator coils are located inside the freezer compartment. Warm air from the fridge circulates around these coils. The refrigerant inside the coils absorbs the heat from this air, causing it to cool. The cooled air then circulates back into the fridge, maintaining a low temperature. A similar process occurs in air conditioning units, where the evaporator cools the air that is then circulated throughout a building.
One key benefit of using evaporators is energy efficiency. Compared to other cooling methods, evaporative cooling can be significantly less energy-intensive, leading to lower operating costs. Another benefit is environmental friendliness, particularly when using natural refrigerants like water. Evaporative coolers don't rely on harmful chemicals, making them a sustainable choice for cooling applications.
A third benefit is versatility. Evaporators are adaptable to various scales and applications, from small residential refrigerators to large-scale industrial processes. They can be used to cool air, liquids, and even solids, making them an indispensable component in many industries.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Evaporators
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Energy Efficient | Can be less effective in humid climates (for evaporative coolers) |
| Environmentally Friendly (with natural refrigerants) | Requires regular maintenance (cleaning, refrigerant checks) |
| Versatile Applications | Can be prone to leaks and corrosion |
Best practices for evaporator operation include regular cleaning of the coils to prevent fouling, proper refrigerant charging, and ensuring adequate airflow. Regular maintenance can significantly improve efficiency and extend the lifespan of the evaporator.
Real-world examples of evaporators include those found in refrigerators, air conditioners, industrial chillers, and desalination plants. Each application leverages the same fundamental principle of heat absorption through evaporation to achieve its specific cooling or concentration objective.
Common challenges related to evaporators include refrigerant leaks, which can be harmful to the environment and reduce cooling efficiency. Solutions include regular leak detection and prompt repair. Another challenge is coil fouling, which can be addressed through regular cleaning and proper filtration.
Frequently asked questions about evaporators include "What is the difference between an evaporator and a condenser?", "What are the different types of refrigerants used?", "How often should I clean my evaporator coils?", and "What are the signs of a malfunctioning evaporator?". Understanding the answers to these questions can help ensure optimal evaporator performance.
Tips and tricks for optimizing evaporator performance include maintaining proper airflow, ensuring adequate refrigerant levels, and scheduling regular maintenance checks. These simple steps can significantly improve efficiency and prolong the lifespan of the evaporator.
In conclusion, the evaporator plays a critical role in a wide range of applications, from keeping our food fresh to enabling complex industrial processes. Understanding its function, benefits, and potential challenges is essential for maximizing its efficiency and ensuring its long-term performance. By implementing best practices and addressing potential issues proactively, we can harness the power of evaporation to achieve efficient and sustainable cooling and concentration solutions. Whether it's the quiet hum of your refrigerator or the massive cooling systems in industrial plants, the evaporator's silent work allows us to enjoy a comfortable and productive environment. Take a moment to appreciate the ingenious simplicity and powerful impact of this often-overlooked component.
Beyond the books exciting cosas que puedes hacer en la escuela
A spark in republic city exploring the relationship between korra and asami
Unlocking the secrets of indonesian vehicle plates your online guide