Unlocking Root Causes: Demystifying the Ishikawa Diagram
In a world brimming with complexity, finding the root cause of a problem can feel like searching for a hidden spring in a vast, overgrown garden. We often find ourselves pruning leaves, hoping for a healthier plant, but the underlying issue remains untouched. What if there were a tool, a map, to guide us through the tangled vines of cause and effect? Enter the Ishikawa Diagram, a powerful visual tool designed to unearth those hidden springs and illuminate the path to true, lasting solutions.
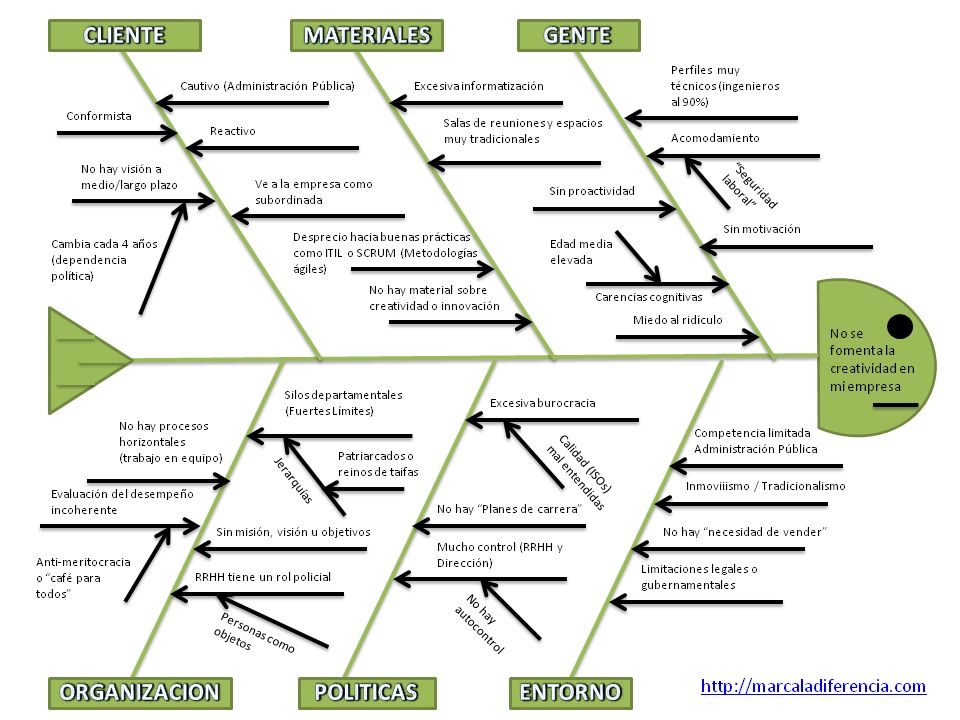
The Ishikawa Diagram, also known as the fishbone diagram or cause-and-effect diagram, provides a structured approach to brainstorming and problem-solving. It's a visual representation that helps us dissect a problem by identifying and categorizing its potential causes. Imagine the skeleton of a fish – the head represents the problem, and the bones branching out represent the various factors contributing to it. This simple yet elegant framework allows us to move beyond superficial symptoms and delve into the underlying issues, fostering a deeper understanding of the challenges we face.
Developed by Kaoru Ishikawa, a Japanese organizational theorist, in the 1960s, the Ishikawa Diagram was initially used in quality control within the manufacturing industry. However, its versatility quickly became apparent, and its application expanded to encompass a wide range of fields, from healthcare and education to business management and personal development. Its enduring popularity speaks volumes about its effectiveness in untangling complex situations and facilitating collaborative problem-solving.
The core principle of the Ishikawa Diagram lies in its ability to break down a problem into manageable categories. These categories, often represented as the "bones" of the fish, can be tailored to the specific context but typically include factors like people, processes, materials, environment, and equipment. This structured approach ensures a comprehensive exploration of potential causes, preventing us from fixating on a single, potentially misleading, factor.
Understanding the historical context and fundamental principles of the Ishikawa Diagram is crucial for harnessing its full potential. It's not merely a diagramming technique; it's a mindset shift, a commitment to digging deeper, to questioning assumptions, and to embracing a collaborative approach to problem-solving. By utilizing this tool, we empower ourselves to move beyond reactive solutions and proactively address the root causes of our challenges.
To construct an Ishikawa Diagram, start by clearly defining the problem you want to address. Write it at the "head" of the fish. Then, identify the main categories of potential causes. These will form the main "bones" branching out from the central line. Brainstorm potential causes within each category, adding them as smaller "bones" branching off the main categories. The process is iterative and encourages collaborative input. Once the diagram is complete, it serves as a visual map for prioritizing and addressing the identified root causes.
One of the primary benefits of using an Ishikawa Diagram is its ability to foster collaboration. The visual nature of the diagram makes it easy for teams to contribute their perspectives and insights, leading to a more comprehensive understanding of the problem and its potential solutions. Additionally, the structured approach helps to avoid biases and encourages a more objective analysis of the situation.
Another key benefit is its visual clarity. The diagram provides a clear and concise overview of the problem and its potential causes, making it easier to identify patterns and prioritize areas for improvement. This visual representation can be particularly helpful in communicating complex issues to stakeholders and facilitating shared understanding.
Finally, the Ishikawa Diagram promotes a proactive approach to problem-solving. By focusing on root causes, we move beyond addressing symptoms and work towards preventing future occurrences of the problem. This proactive stance can lead to more sustainable and impactful solutions.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Ishikawa Diagrams
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Facilitates collaborative brainstorming | Can become overly complex for multi-faceted problems |
| Provides a visual representation of complex issues | May not effectively identify relationships between causes |
| Encourages a focus on root causes | Requires active participation and open communication from all involved |
In conclusion, the Ishikawa Diagram, a seemingly simple tool, offers a profound approach to problem-solving. By visually mapping the cause-and-effect relationship, it empowers individuals and teams to move beyond superficial solutions and address the root of their challenges. Whether you're streamlining a business process, improving team dynamics, or simply trying to understand a recurring personal issue, the Ishikawa Diagram offers a powerful framework for achieving clarity, fostering collaboration, and driving meaningful change. Embrace this tool, and unlock the potential for deeper understanding and more impactful solutions.
Unlocking ea fc 24 potential live editor enhancements
Unlocking your best self a guide to personal care essentials
The allure of pearls a deep dive into pearl necklaces