Unlocking Product Creation: Exploring RBT Form 3 Chapter 2
Ever wonder how that perfect notebook or that addictive app came into being? It's not magic, it's product development, and it's exactly what RBT Form 3 Chapter 2, focusing on product creation, dives into. This crucial area of study in the Malaysian education system equips students with the foundational knowledge needed to understand the entire lifecycle of a product, from initial concept to the final market release. So, buckle up as we explore the fascinating world of bringing ideas to life.
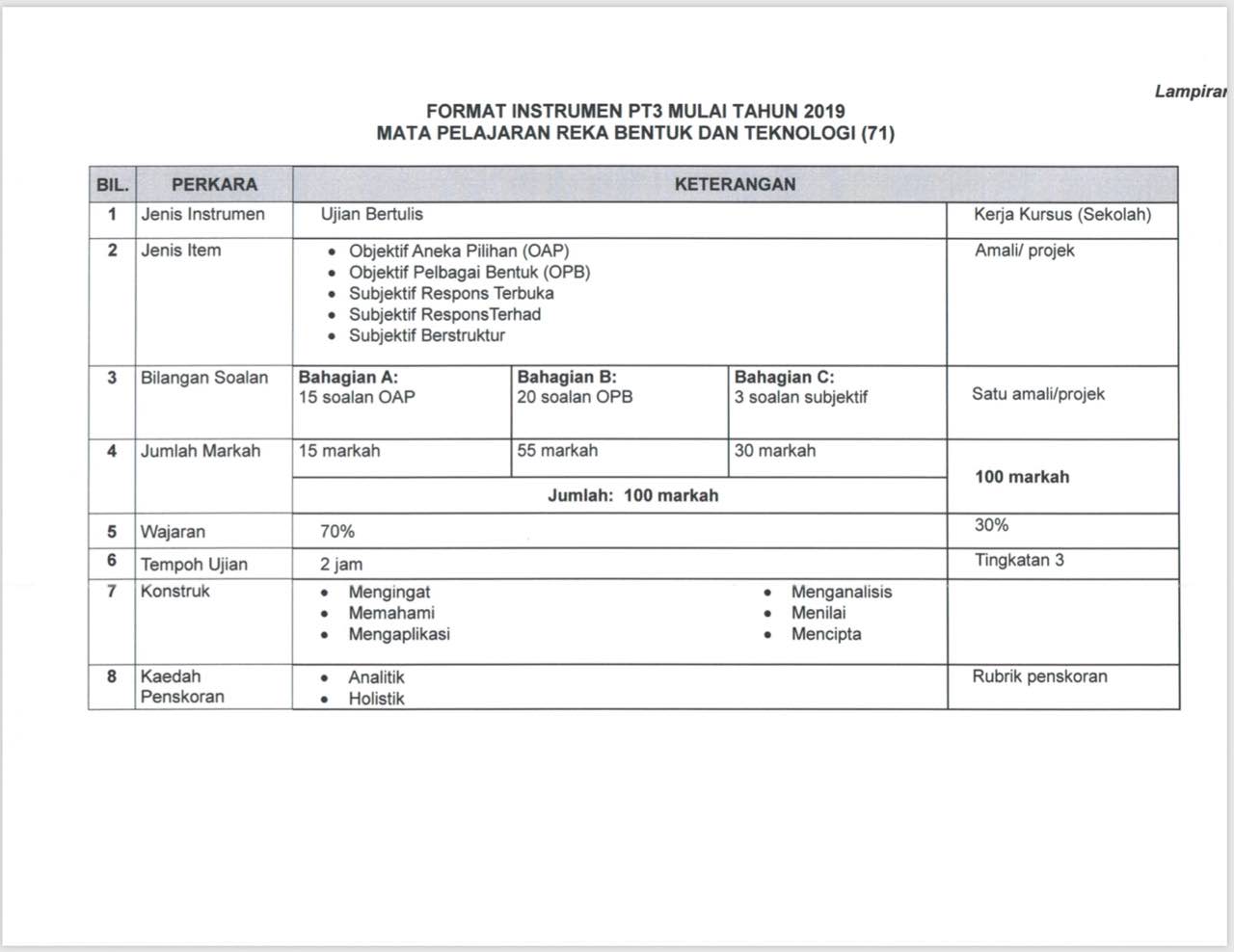
This chapter in the Reka Bentuk dan Teknologi (RBT) syllabus isn't just about making things; it's about understanding the process, the market, and the consumer. It covers everything from brainstorming product ideas and selecting the right materials to planning the production process and eventually marketing the final product. It's a holistic approach that emphasizes problem-solving and creative thinking within a practical framework.
Imagine a world without innovation, a world stuck with the same old products. That's the world RBT Form 3 Chapter 2 aims to prevent by cultivating the next generation of innovators. By emphasizing product output, students gain practical skills and develop an understanding of the vital role product development plays in economic growth and societal advancement. This knowledge is not only beneficial for aspiring entrepreneurs but also for anyone seeking to understand how things are made and how they can contribute to a more innovative future.
The core of RBT Form 3 Chapter 2 lies in understanding the process of transforming an idea into a tangible product. It delves into the different stages of product development, from identifying a need or problem in the market to designing, prototyping, and testing potential solutions. It encourages students to think critically about the materials they choose, the production methods they employ, and the impact their products will have on the environment and the consumer.
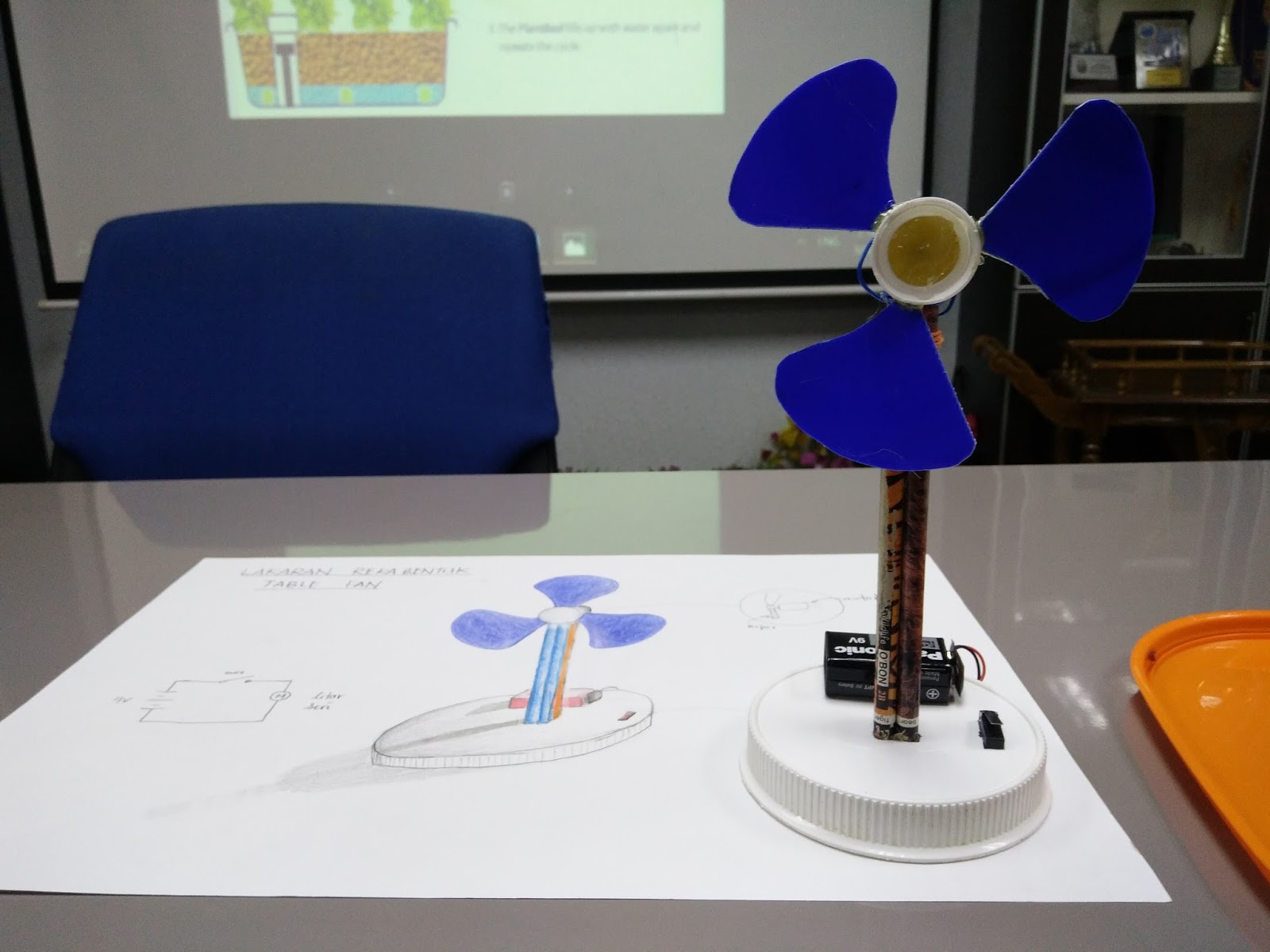
A key aspect of this curriculum is its emphasis on practical application. Students aren't just learning theory; they're actively involved in creating their own products, applying the concepts they learn to real-world scenarios. This hands-on approach fosters creativity, problem-solving skills, and a deeper understanding of the challenges and rewards of bringing a product to life.
The history of product development is as old as humanity itself, evolving from basic tools and necessities to the complex technologies we rely on today. RBT Form 3 Chapter 2 builds upon this history, connecting traditional craftsmanship with modern manufacturing techniques. The importance of this subject lies in its potential to empower students with the skills and knowledge needed to shape the future of product design and innovation.
A simple example could be designing a more ergonomic school bag. Students might analyze existing designs, identify common problems like back pain, and then develop a new bag with improved weight distribution and adjustable straps. This practical application reinforces the core concepts of the chapter.
Benefits of mastering the concepts in RBT Form 3 Chapter 2 include enhanced creativity, improved problem-solving skills, and a deeper understanding of the product development process. These skills are highly valuable in various fields, from engineering and design to marketing and entrepreneurship.
Creating an action plan might involve identifying a market need, brainstorming product ideas, sketching initial designs, creating a prototype, testing the prototype, refining the design, and finally, developing a marketing strategy. A successful example could be a student team developing a phone stand from recycled materials, demonstrating both innovation and sustainability.
One of the challenges students might face is a lack of access to certain materials or tools. A solution could involve exploring alternative materials or utilizing readily available resources within their environment. For example, using cardboard instead of plastic or utilizing online design tools if specialized software is unavailable.
FAQ: What is the purpose of prototyping? How do you choose the right materials for a product? What are the different stages of product development? What are some effective marketing strategies for new products? What is the importance of cost analysis in product creation? How can you protect your product design? How do you evaluate the success of a product? What are the environmental considerations in product development?
A valuable tip is to thoroughly research the target market before finalizing a product design. Understanding the needs and preferences of the consumer is crucial for developing a successful product.
In conclusion, RBT Form 3 Chapter 2 on product output is a vital component of the Malaysian education system, providing students with a comprehensive understanding of the product development process. From ideation to marketing, the chapter equips students with the tools and knowledge they need to become innovative thinkers and problem-solvers. By fostering creativity and practical skills, this curriculum prepares students to contribute meaningfully to the economy and society, shaping a future filled with innovative and impactful products. Understanding these concepts is crucial not only for those aspiring to careers in design and engineering but also for anyone seeking to understand how products are created and how they impact our daily lives. This foundational knowledge empowers individuals to be informed consumers, creative problem-solvers, and potentially, the next generation of innovators. Embrace the challenge, explore the possibilities, and let your creativity flourish. The future of product development awaits.
Bastognes american cemetery a story etched in stone
Unlocking the potential of fifa 23 ultimate team squad construction
Unleash your inner gridiron mage epic fantasy football names with a dd twist