Unlocking Circuit Secrets: Mastering Phasor Diagrams for RC Circuits
Ever wondered how electrical engineers make sense of the complex dance of voltages and currents in alternating current (AC) circuits? One of their most powerful tools is the phasor diagram, a graphical representation that simplifies AC circuit analysis, particularly for circuits containing resistors and capacitors, known as RC circuits. This article will illuminate the world of phasor diagrams for RC circuits, revealing their utility and providing practical guidance for their application.
Imagine trying to track the constantly changing voltages and currents in an AC circuit. It's like trying to follow a swarm of bees! Phasor diagrams provide a way to freeze this motion, representing these sinusoidal quantities as rotating vectors, or phasors. By visualizing the relationship between voltage and current phasors, we can gain a deeper understanding of circuit behavior, including phase differences, impedance, and power consumption.
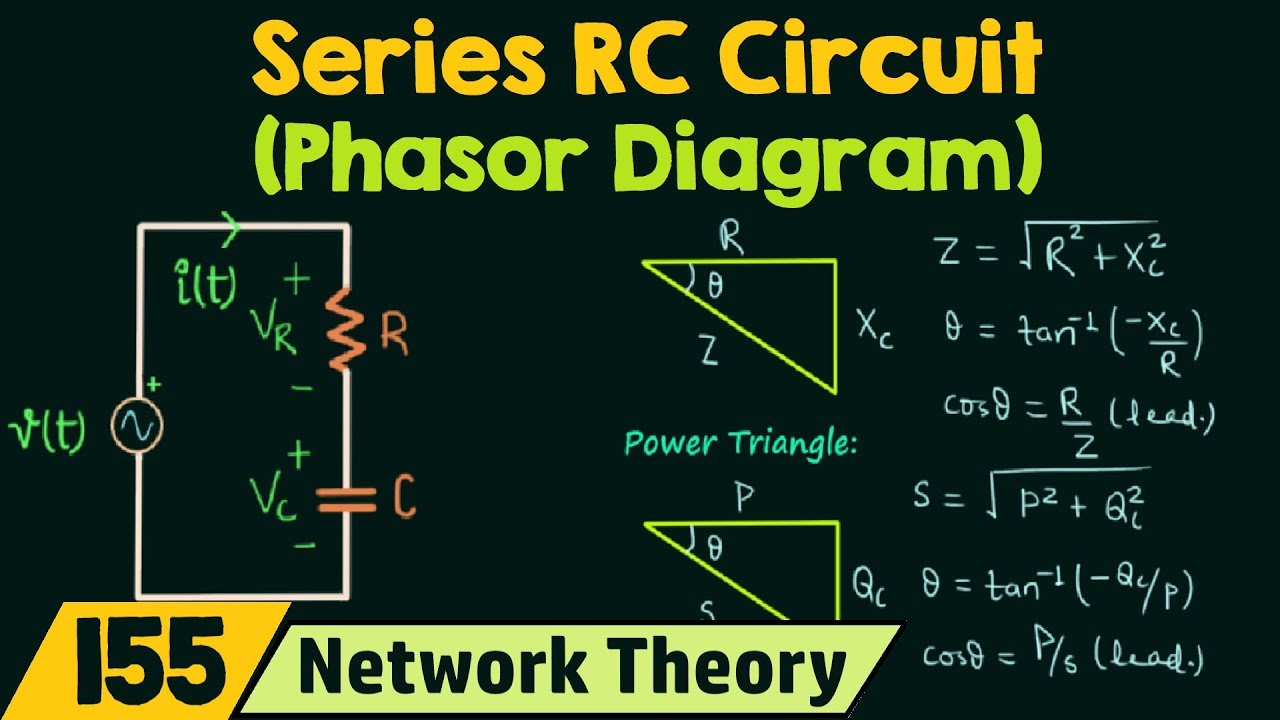
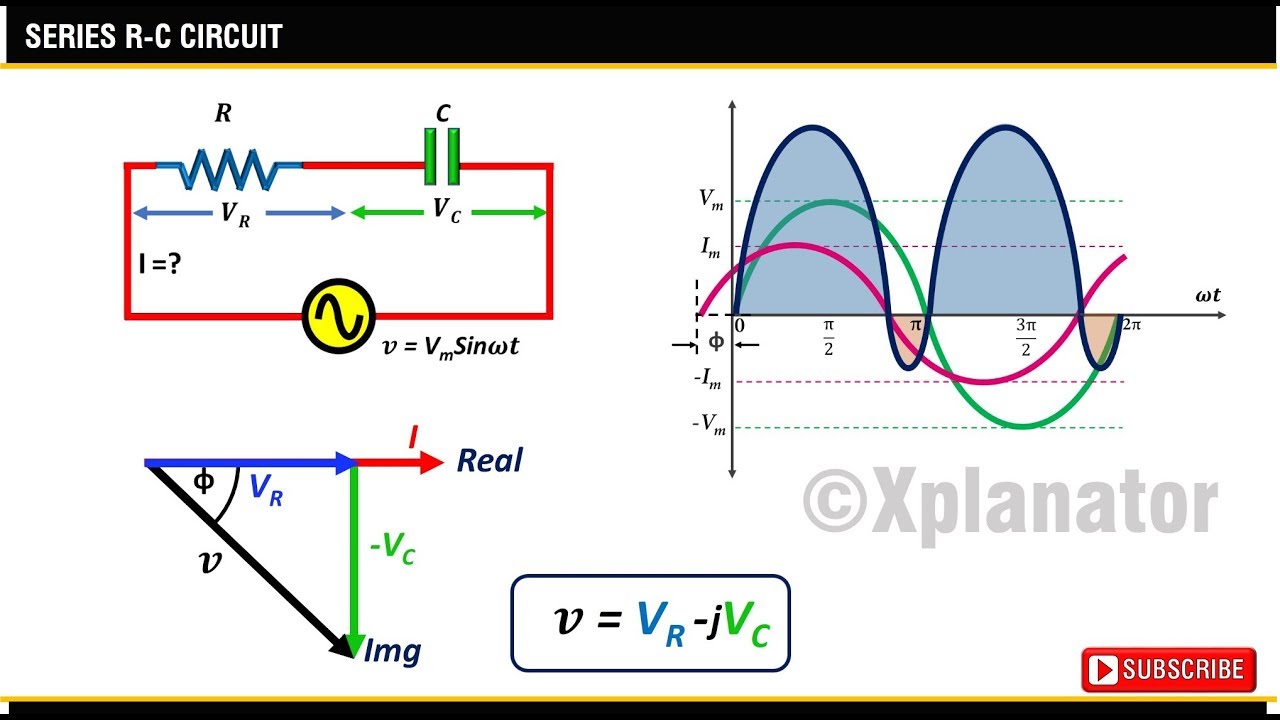
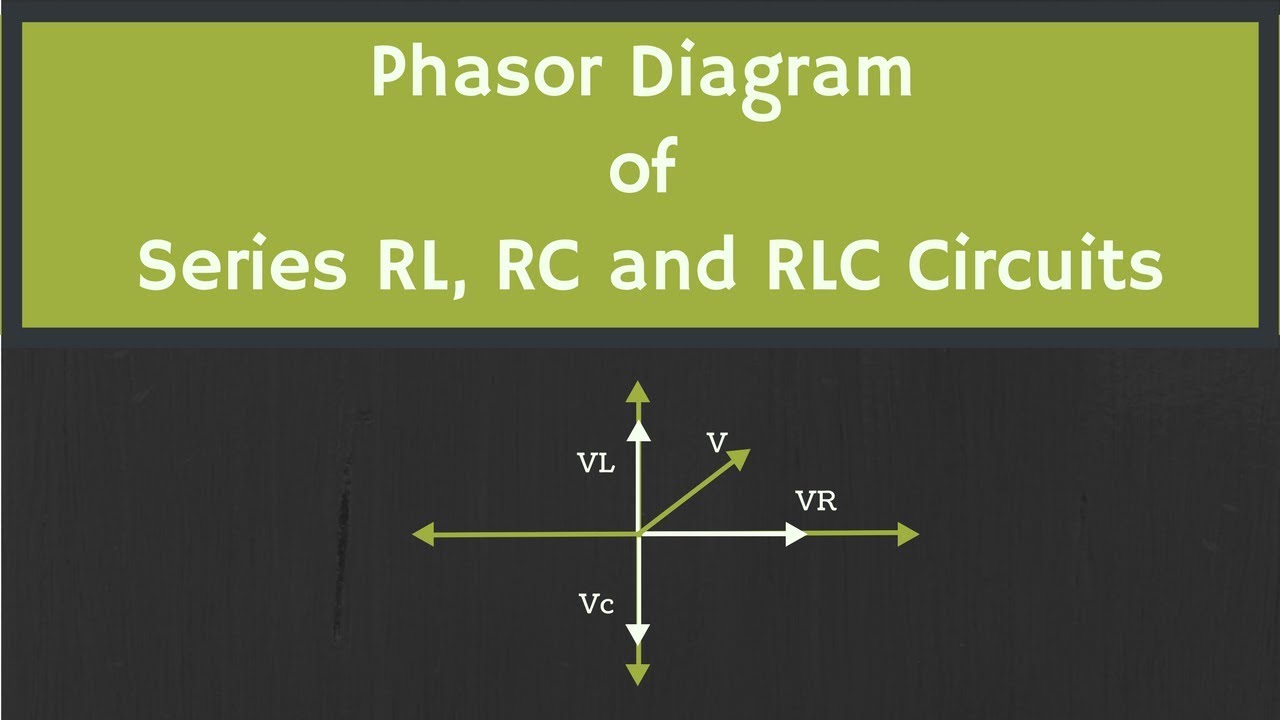
The concept of phasors arises from the mathematical representation of sinusoidal waves using complex numbers. This allows us to replace complicated trigonometric calculations with simpler algebraic operations. In the context of an RC circuit, the resistor voltage and current are in phase, while the capacitor voltage lags behind the current. This phase difference is clearly depicted in the RC circuit phasor diagram.
Phasor diagrams for RC circuits have a rich history, originating from the development of AC circuit theory in the late 19th century. Charles Proteus Steinmetz, a prominent electrical engineer, played a significant role in popularizing the use of phasors. These diagrams quickly became indispensable for analyzing and designing AC power systems, contributing to the rapid electrification of the world. Today, their relevance continues to grow as we grapple with increasingly complex electronic circuits.
A fundamental issue addressed by phasor diagrams in RC circuits is the phase difference between the voltage across the capacitor and the current flowing through it. This phase shift arises due to the capacitor's inherent property of storing energy in an electric field. The phasor diagram visually represents this phase difference, typically showing the capacitor voltage lagging the current by 90 degrees. Understanding this phase relationship is crucial for calculating circuit impedance, power factor, and other important parameters.
A simple example illustrates the power of phasor diagrams. Consider an RC circuit connected to an AC source. The phasor diagram will show the resistor voltage and current in phase along the horizontal axis, while the capacitor voltage phasor points downwards, indicating a 90-degree lag. The total voltage across the circuit is then the vector sum of the resistor and capacitor voltages. This graphical approach simplifies the calculation of the circuit's total impedance and phase angle.
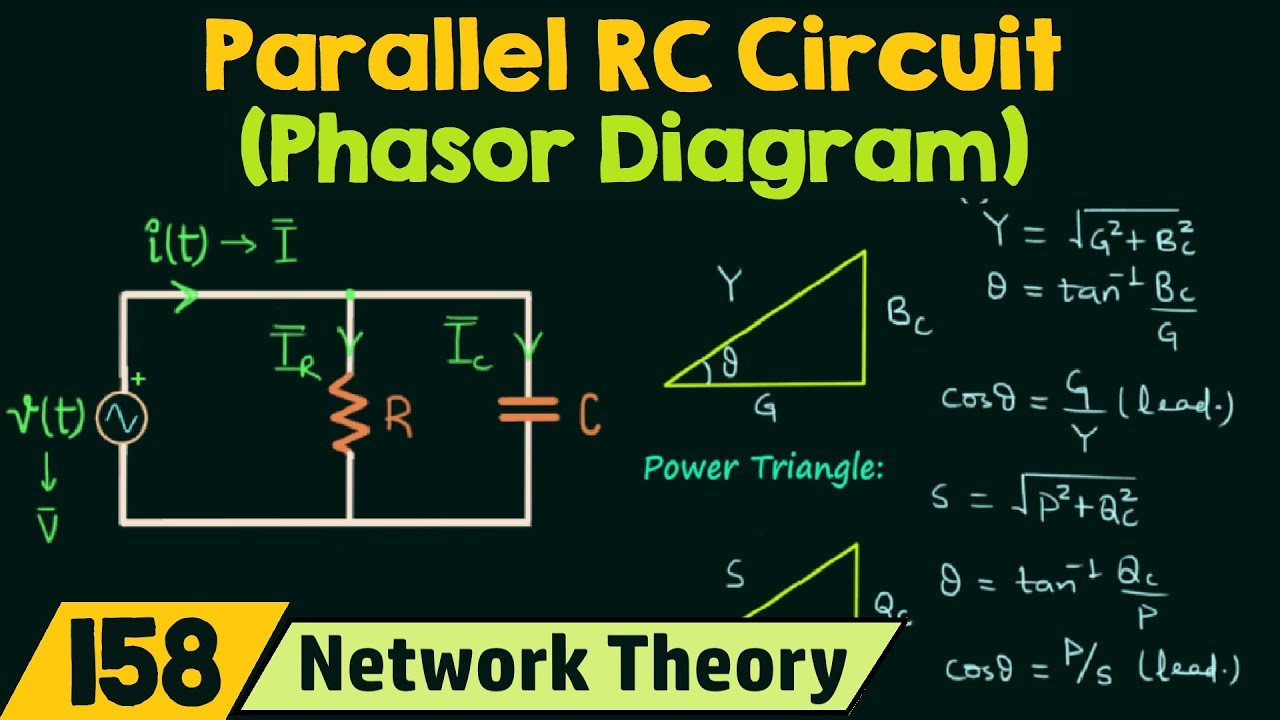
Benefits of using phasor diagrams for RC circuit analysis include simplified calculations, clear visualization of phase relationships, and easier understanding of circuit behavior. For example, by inspecting the phasor diagram, we can easily determine the leading or lagging nature of voltage and current. This is crucial for optimizing power transfer and minimizing reactive power in AC circuits.
A typical action plan for using phasor diagrams involves: 1) Identifying the circuit components and their values. 2) Drawing the individual voltage and current phasors based on their phase relationships. 3) Combining the phasors vectorially to determine the overall circuit voltage and current. 4) Analyzing the resulting phasor diagram to determine circuit impedance, phase angle, and other parameters.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Phasor Diagram Analysis
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Simplifies AC circuit analysis | Limited to steady-state sinusoidal conditions |
| Visualizes phase relationships | Can become complex for large circuits |
| Facilitates impedance calculations | Does not provide information about transient behavior |
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What is a phasor? A phasor is a rotating vector representing a sinusoidal quantity.
2. Why are phasor diagrams used? They simplify AC circuit analysis.
3. What is the phase relationship in an RC circuit? Capacitor voltage lags current by 90 degrees.
4. How do you construct a phasor diagram? Represent voltages and currents as vectors with appropriate magnitudes and phase angles.
5. What does the length of a phasor represent? The magnitude of the sinusoidal quantity.
6. What does the angle of a phasor represent? The phase angle of the sinusoidal quantity.
7. How can phasor diagrams help in power factor correction? They visually show the phase difference between voltage and current, which is key for power factor correction.
8. What are some alternative methods for AC circuit analysis? Other methods include using complex numbers directly or using time-domain analysis.
In conclusion, phasor diagrams are invaluable tools for analyzing RC circuits. They provide a clear and concise way to visualize the relationships between voltages and currents, simplifying calculations and enabling a deeper understanding of circuit behavior. By mastering this technique, you gain a powerful tool for tackling a wide range of electrical engineering challenges. As you delve deeper into circuit analysis, remember the power of the phasor diagram – a visual key to unlocking the secrets of AC circuits. Explore further resources and continue practicing with different RC circuit configurations to solidify your understanding and unlock the full potential of this essential technique.
The warmth of digital peaches exploring the peach color code
Duramax v6 turbo diesel unleash the beast within your truck
Ocean county courthouse toms river nj your guide