Unlocking AC Circuit Secrets: Mastering Phasor Diagrams
Ever feel lost navigating the complex world of alternating current (AC) circuits? Understanding the fluctuating voltages and currents can be a real headache. But what if there was a visual tool that could simplify these intricate concepts? Enter the phasor diagram – a powerful graphical representation that unlocks the secrets of AC circuit behavior.
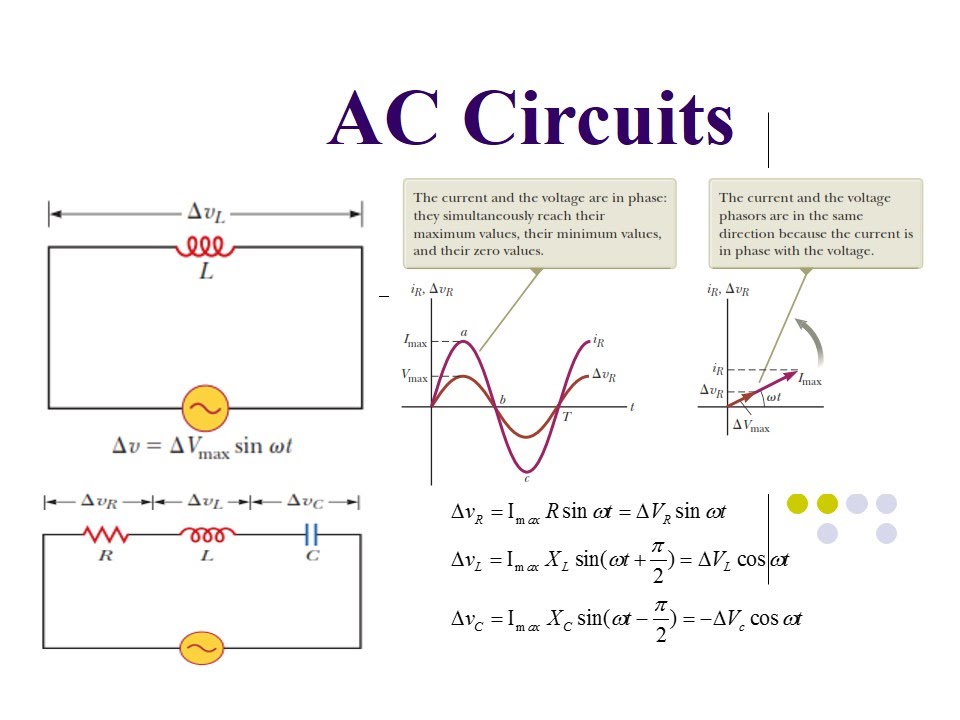
Phasor diagrams provide a snapshot of AC circuit quantities at a specific instant in time. They transform sinusoidal waveforms into rotating vectors, called phasors, making it easier to visualize the relationship between voltage and current. This article serves as your comprehensive guide to understanding and creating phasor diagrams, from the fundamental principles to advanced techniques.
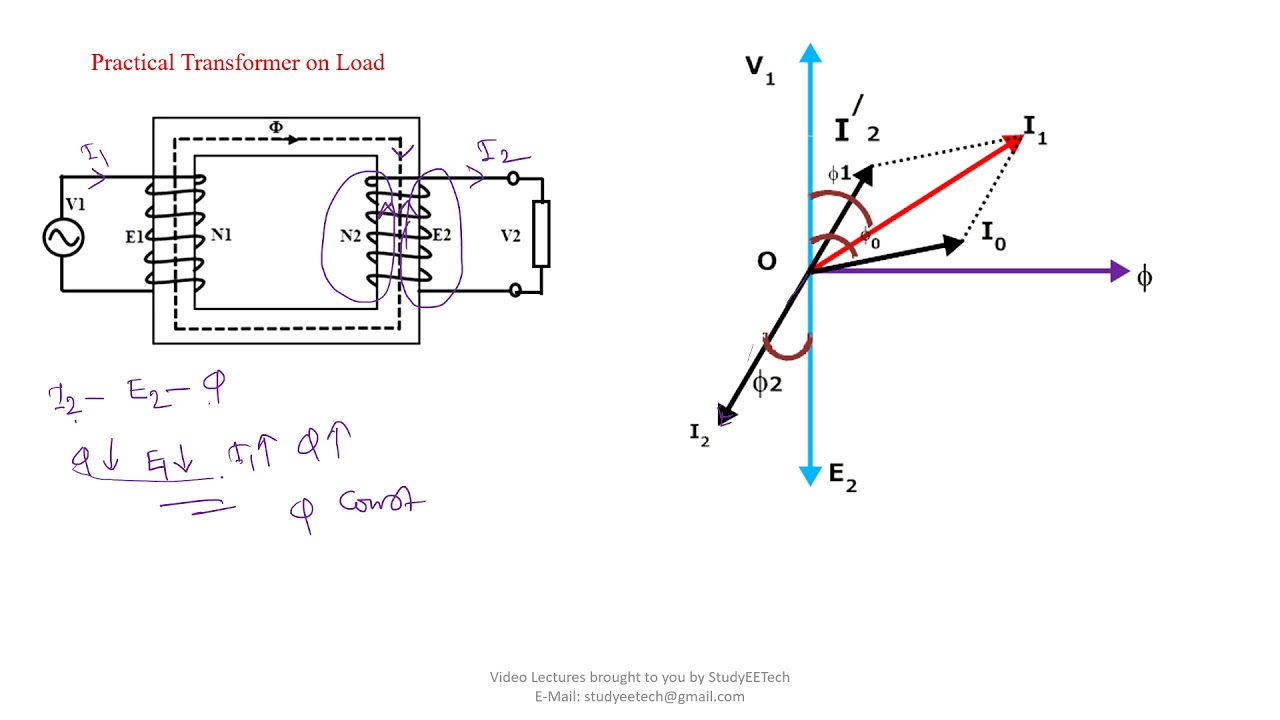
Creating a phasor diagram involves representing AC quantities as vectors. The length of the vector corresponds to the magnitude of the quantity (voltage or current), while the angle represents its phase shift relative to a reference. By plotting these vectors on a complex plane, we can visually analyze the phase relationships and calculate circuit parameters.
Historically, Charles Proteus Steinmetz, a renowned electrical engineer, pioneered the use of phasor diagrams in the late 19th century. He recognized the power of this visual approach for simplifying AC circuit analysis. Prior to phasor diagrams, analyzing AC circuits relied heavily on complex mathematical calculations, making the process cumbersome and time-consuming.
The importance of phasor diagrams in electrical engineering cannot be overstated. They are fundamental to understanding the behavior of AC circuits, particularly in power systems, electronics, and communication systems. Constructing phasor diagrams accurately is crucial for designing and troubleshooting circuits effectively. Common issues encountered when creating phasor diagrams include incorrect scaling of magnitudes, inaccurate representation of phase angles, and difficulty visualizing the rotating vectors.
One of the main benefits of constructing phasor diagrams is the simplified analysis of complex AC circuits. By visually representing the phase relationships between voltage and current, we can easily determine circuit impedance, power factor, and other important parameters. Another advantage is the ability to visualize the effect of adding or subtracting AC quantities with different phases. This is particularly useful in analyzing circuits with multiple voltage or current sources.
To create a phasor diagram, follow these steps: 1. Identify the AC quantities to be represented. 2. Determine the magnitude and phase angle of each quantity. 3. Draw a set of axes representing the complex plane. 4. Plot each quantity as a vector, with the length corresponding to the magnitude and the angle corresponding to the phase. 5. Analyze the resulting diagram to determine the relationships between the quantities.
For example, consider a simple circuit with a resistor and an inductor in series. The voltage across the resistor is in phase with the current, while the voltage across the inductor leads the current by 90 degrees. The phasor diagram for this circuit would show two vectors, one representing the resistor voltage and the other representing the inductor voltage. The inductor voltage vector would be rotated 90 degrees counterclockwise relative to the resistor voltage vector.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Phasor Diagrams
While powerful, phasor diagrams have limitations:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Simplified AC circuit analysis | Limited to steady-state conditions |
| Visual representation of phase relationships | Cannot directly represent transient behavior |
| Easy calculation of circuit parameters | Requires understanding of complex numbers |
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What is a phasor? A phasor is a rotating vector representing a sinusoidal quantity.
2. Why are phasor diagrams useful? They simplify AC circuit analysis.
3. How do you determine the phase angle of a phasor? From the time shift of the sinusoidal waveform.
4. What is the significance of the length of a phasor? It represents the magnitude of the AC quantity.
5. Can phasor diagrams be used for DC circuits? No, they are specifically for AC circuits.
6. What is the relationship between phasors and complex numbers? Phasors can be represented mathematically using complex numbers.
7. How do you add phasors? Graphically or using complex number addition.
8. What are some common mistakes when drawing phasor diagrams? Incorrect scaling and inaccurate phase angles.
Tips and tricks for drawing phasor diagrams include using graph paper for accurate scaling, clearly labeling the axes and vectors, and double-checking the phase angles.
In conclusion, mastering the art of creating phasor diagrams is essential for anyone working with AC circuits. This powerful tool simplifies complex analysis, provides a visual understanding of phase relationships, and enables efficient circuit design and troubleshooting. From visualizing the interplay of voltage and current to calculating crucial circuit parameters, phasor diagrams are indispensable in electrical engineering. Embrace this technique and unlock a deeper understanding of the fascinating world of AC circuits. By utilizing the principles and strategies outlined in this guide, you can confidently tackle even the most challenging AC circuit problems. So, grab your pencil, graph paper, and dive into the world of phasor diagrams – you'll be amazed at the insights they reveal. Don't forget to practice regularly, and soon you'll be a phasor diagram pro!
Sofia sanchez shining a light on down syndrome
Luke combs utah tickets your guide to snagging seats on ticketmaster
Conquering granites hard water nemesis a comprehensive guide