Conquer AP Physics C Circular Motion FRQs: Ace the Exam
Ready to tackle one of the most challenging, yet rewarding, topics in AP Physics C? Circular motion is a cornerstone of mechanics, and mastering it is essential for success on the exam, especially the free-response questions (FRQs). These questions often demand a deep understanding of the concepts and the ability to apply them to complex scenarios. Let's dive in and unravel the mysteries of circular motion.
Circular motion problems in AP Physics C aren't just about plugging numbers into formulas. They require a nuanced understanding of how forces interact to create and maintain circular paths. From a car navigating a banked curve to a satellite orbiting Earth, the principles of circular motion govern a wide range of phenomena. The AP Physics C exam tests your ability to analyze these situations, derive necessary equations, and arrive at solutions using calculus.
The AP Physics C curriculum draws heavily upon the historical development of circular motion concepts, beginning with Newton’s laws and extending to more complex applications involving rotational dynamics and energy conservation. Understanding the historical context can enrich your comprehension of these principles. One of the key challenges in tackling circular motion FRQs lies in correctly identifying the forces involved, resolving them into radial and tangential components, and applying Newton’s second law in both directions. This often involves dealing with non-constant forces, requiring the use of calculus to analyze the motion.
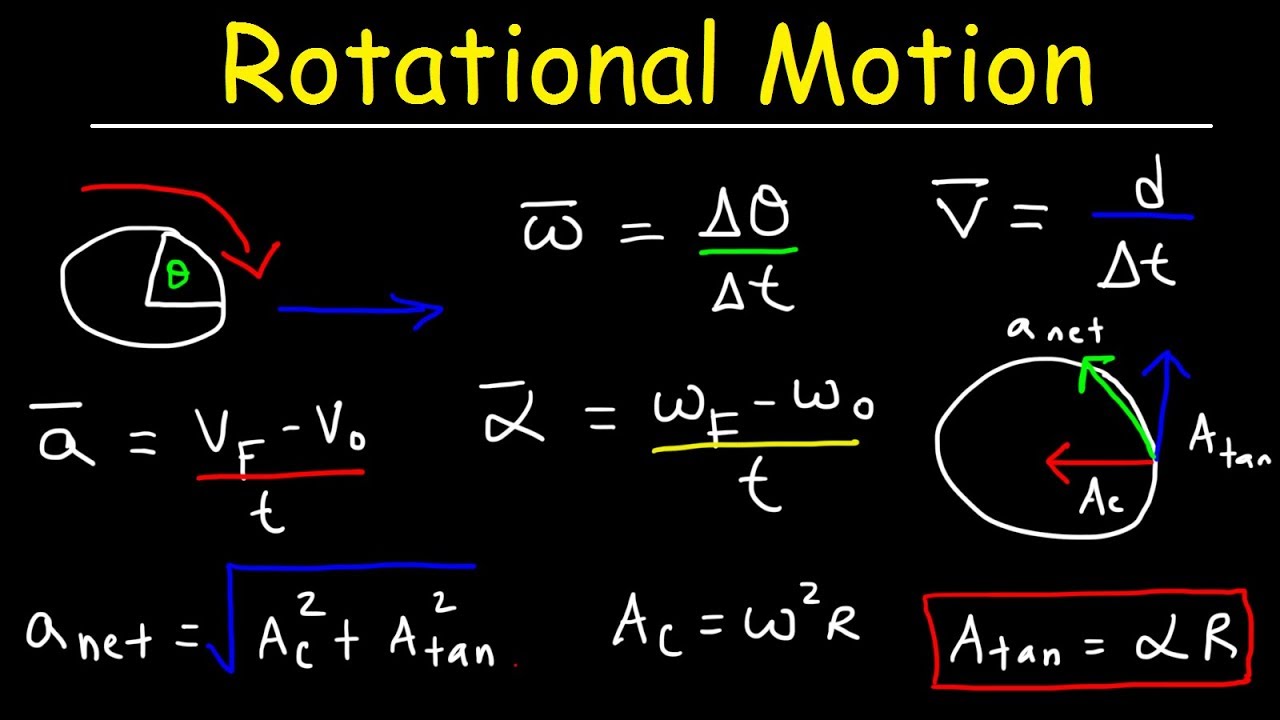
At its core, circular motion describes the movement of an object along a circular path. Uniform circular motion, a common focus in AP Physics C, implies a constant speed but a changing velocity due to the constantly changing direction. This change in velocity results in centripetal acceleration, always directed toward the center of the circle. The force responsible for this acceleration is the centripetal force, which can manifest as tension, gravity, friction, or a combination thereof.
A simple example of uniform circular motion is a ball tied to a string and swung in a horizontal circle. The tension in the string provides the centripetal force, keeping the ball moving in a circular path. A more complex example involves analyzing the motion of a car on a banked curve, where both the normal force and friction contribute to the centripetal force.
Successfully navigating AP Physics C circular motion problems hinges on a solid grasp of several key concepts: centripetal force, centripetal acceleration, angular velocity, period, and frequency. Familiarizing yourself with these concepts and their interrelationships is vital for deciphering and solving complex FRQs.
One effective approach to mastering these problems is breaking them down systematically. Start by drawing a free-body diagram, clearly identifying all forces acting on the object. Next, resolve these forces into their radial and tangential components. Apply Newton's second law in the radial direction to analyze the centripetal force and acceleration. If the speed is not constant, analyze the tangential forces to determine the tangential acceleration and how the speed changes over time.
Effective preparation for circular motion FRQs requires consistent practice. Working through a variety of problems, from simple uniform circular motion to more complex scenarios involving non-uniform motion and changing forces, is essential. Analyze solutions, understand the underlying principles, and identify areas for improvement.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Focusing on Circular Motion FRQs
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Strong foundation in core mechanics concepts | Can be mathematically challenging |
| Prepares for more advanced physics topics | Requires strong problem-solving skills |
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What is centripetal force? (Answer: The force directed towards the center of the circle that keeps an object moving in a circular path.)
2. What is the difference between speed and velocity in circular motion? (Answer: Speed is constant in uniform circular motion, while velocity changes constantly due to the changing direction.)
3. How is centripetal acceleration related to velocity and radius? (Answer: a = v²/r)
4. What is the role of calculus in circular motion problems? (Answer: Calculus is essential for analyzing non-uniform circular motion where forces and acceleration may vary.)
5. What are some common types of forces that act as centripetal forces? (Answer: Tension, gravity, friction, normal force)
6. How do I approach a circular motion FRQ? (Answer: Draw a free-body diagram, resolve forces, apply Newton's second law.)
7. What resources can I use to practice circular motion problems? (Answer: Your textbook, AP Physics C review books, online resources.)
8. How can I improve my understanding of circular motion concepts? (Answer: Focus on understanding the underlying principles, work through various examples, and seek help when needed.)
In conclusion, mastering circular motion is essential for succeeding on the AP Physics C exam. By understanding the core concepts, practicing consistently, and developing a systematic approach to problem-solving, you can confidently tackle even the most challenging FRQs. Don't be intimidated by the complexity of circular motion – embrace the challenge and reap the rewards of a deeper understanding of physics. Start preparing today and unlock your full potential on the AP Physics C exam!
Unleash your inner scribe old english letters printable free
Mastering case conversion in python the power of lowercase
Electrifying nights diving deep into the world of monday night raw