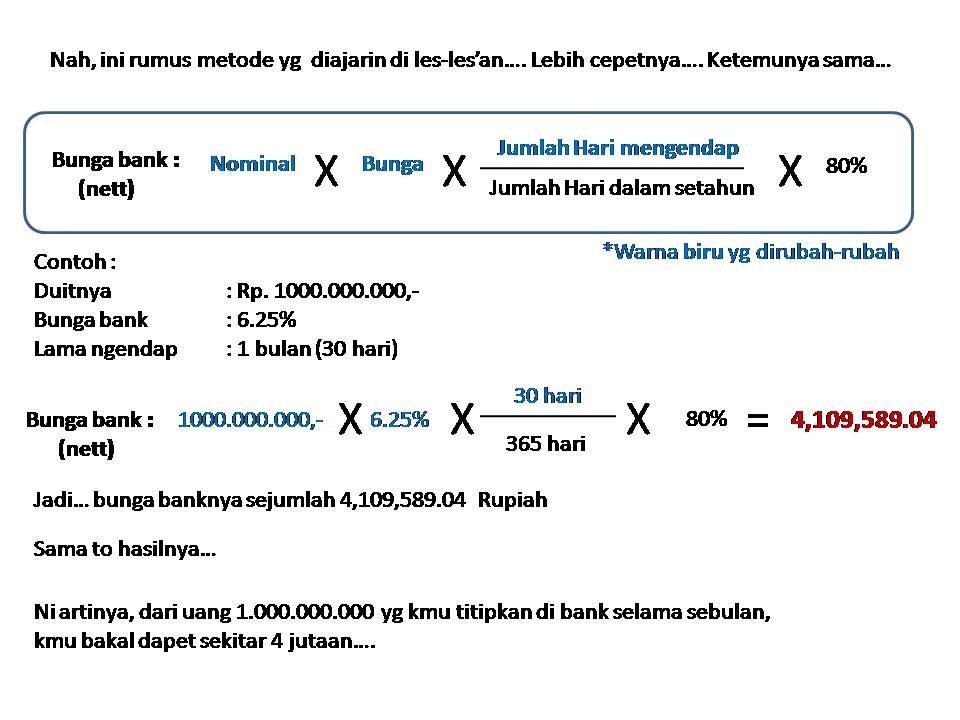
Calculating Annual Bank Interest: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding how your money grows (or shrinks) in a bank account is crucial for effective financial planning. This comprehensive guide will delve into the methods for calculating annual bank interest, empowering you to make informed decisions about your savings and investments.
Calculating bank interest is fundamental to understanding the time value of money. Whether you're saving for a down payment, retirement, or simply want to track your financial progress, knowing how to determine the interest earned or paid on your accounts is essential. This guide will equip you with the knowledge to accurately assess your financial growth.
The concept of interest dates back to ancient civilizations, where it was primarily associated with lending and borrowing agricultural commodities. Over time, the practice evolved and became a cornerstone of modern banking and finance. Accurately determining interest income or expense became crucial for individuals and businesses alike, leading to the development of various calculation methods.
One of the main issues surrounding bank interest calculations is the potential for compounding. Compounding occurs when earned interest is added to the principal, and subsequent interest calculations are based on the new, higher balance. This can significantly impact long-term returns, and understanding its effect is vital for maximizing your savings potential. While seemingly complex, the underlying principles are straightforward, and we'll break them down step-by-step.
Another issue is understanding the difference between nominal interest rate and effective annual interest rate (EAR). The nominal rate is the stated rate, while the EAR considers the compounding frequency. Knowing the difference is crucial for accurately comparing different savings products or loan options. This guide will explain how to calculate both and emphasize their significance in your financial decisions.
The simplest form of interest calculation is simple interest, calculated as: Principal * Interest Rate * Time. For example, $1000 at 5% annual interest for one year yields $50. However, most banks use compound interest. For annual compounding, the formula is: Future Value = Principal * (1 + Interest Rate)^Time. So, $1000 at 5% compounded annually for two years becomes $1102.50.
Understanding annual bank interest calculation has several benefits. Firstly, it allows you to project your future savings, assisting in goal setting. Secondly, it enables you to compare different savings accounts and choose the most profitable option. Lastly, understanding interest calculations can help you manage debt effectively, minimizing interest expenses. For example, by understanding how quickly debt grows with high interest, you can prioritize high-interest debt repayment.
To create an action plan for maximizing your returns, start by listing your financial goals and timelines. Then, research various savings products and compare their interest rates and compounding frequencies. Use the interest calculation methods discussed to project your potential earnings and choose the best option aligned with your goals. A successful example would be choosing a high-yield savings account with frequent compounding for short-term goals and considering long-term investment options like bonds or stocks for retirement.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Calculating Bank Interest
While calculating bank interest is crucial, it’s important to understand both the advantages and disadvantages.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Informed financial decisions | Complexity with compounding |
| Better savings planning | Potential for miscalculation |
Five best practices for calculating and utilizing bank interest effectively include: 1) Understand the difference between simple and compound interest. 2) Learn about the effective annual rate (EAR). 3) Use online calculators or spreadsheets to simplify calculations. 4) Regularly review and adjust your savings strategy. 5) Consult with a financial advisor for personalized advice.
Real-world examples include: 1) Saving for a down payment on a house. 2) Growing a retirement fund. 3) Managing debt effectively. 4) Comparing different loan options. 5) Investing in certificates of deposit (CDs).
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What is the difference between simple and compound interest?
2. How do I calculate the effective annual rate (EAR)?
3. What are the best savings accounts for maximizing interest?
4. How often is interest typically compounded?
5. What is the impact of inflation on interest earnings?
6. How can I minimize interest paid on loans?
7. Where can I find reliable interest rate information?
8. What are some common mistakes to avoid when calculating interest?
One valuable tip is to automate your savings by setting up regular transfers to your high-yield savings account. This consistent approach will leverage the power of compounding and help you achieve your financial goals faster.
In conclusion, understanding how to calculate annual bank interest is an essential financial skill. By grasping the core concepts of interest calculation, compounding, and EAR, you can make informed decisions about your savings, investments, and debt management. Leveraging online tools and resources and adopting best practices can empower you to achieve your financial goals effectively. This knowledge not only helps you make smart financial choices, but also provides you with the confidence to navigate the complex world of banking and finance. Start applying these principles today to take control of your financial future. By actively engaging with your finances and making informed decisions, you pave the way for long-term financial security and success. Don't hesitate to seek professional advice when needed, and remember that consistent effort and a clear understanding of these principles are key to achieving your financial aspirations.
Level up your game the ultimate guide to dd npc character generators
Expressing sympathy ripley funeral home ripley ms flowers
Sad person meme template the dark soul of the internets humor